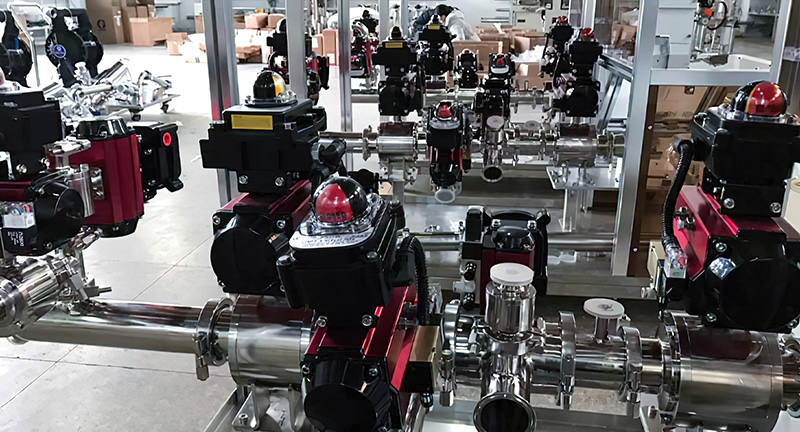
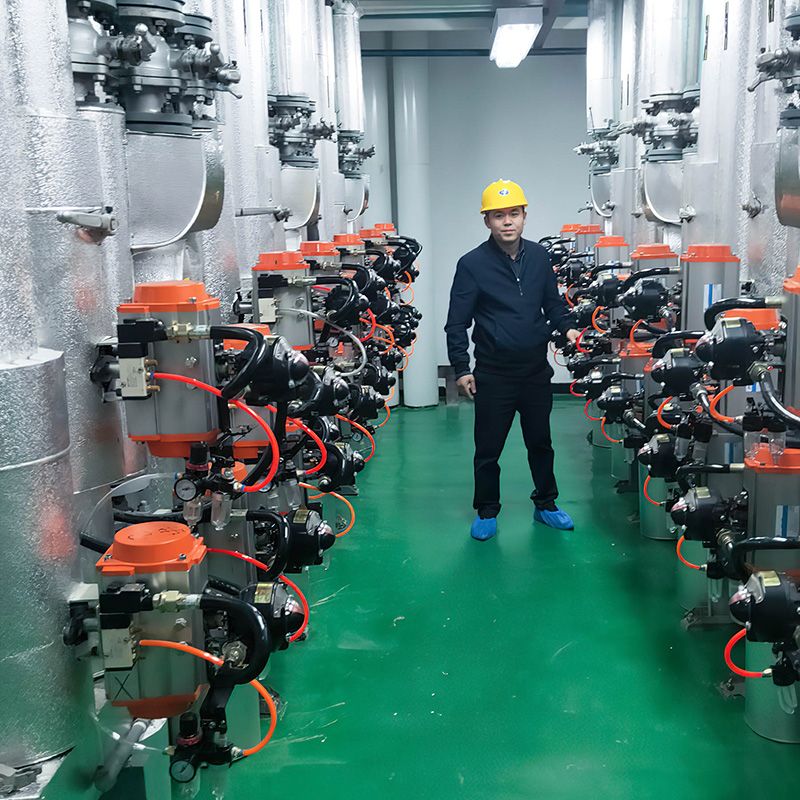
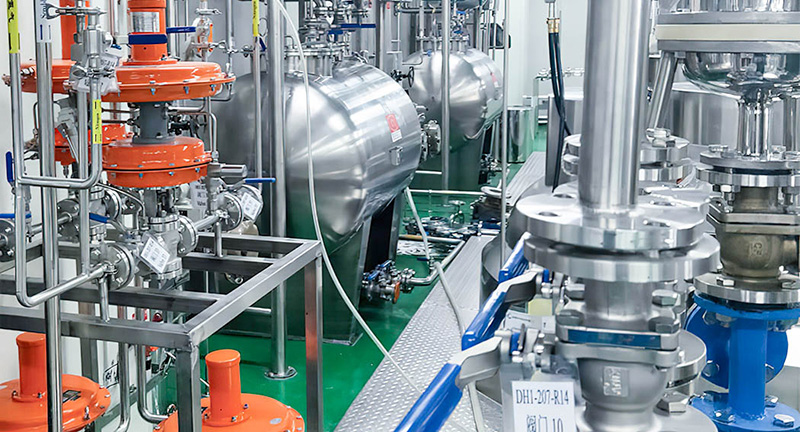

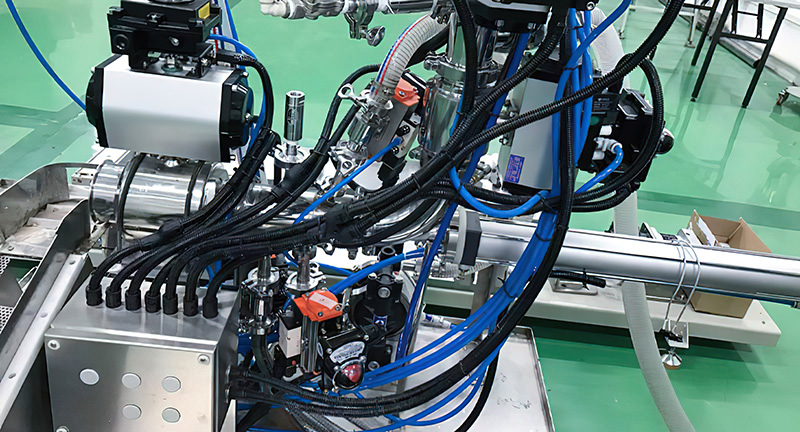
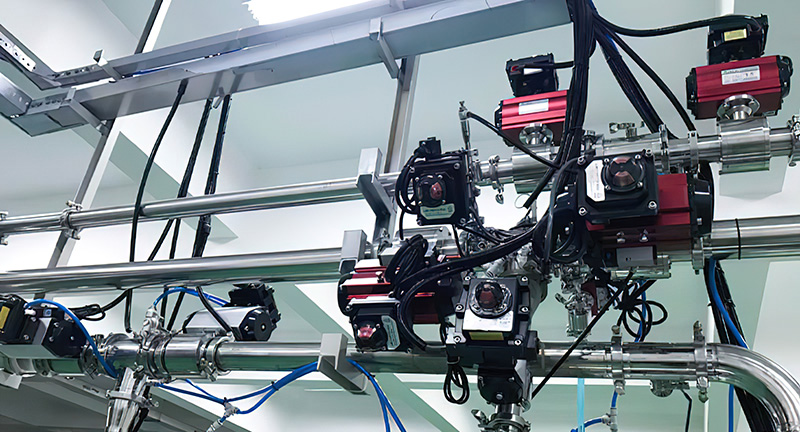
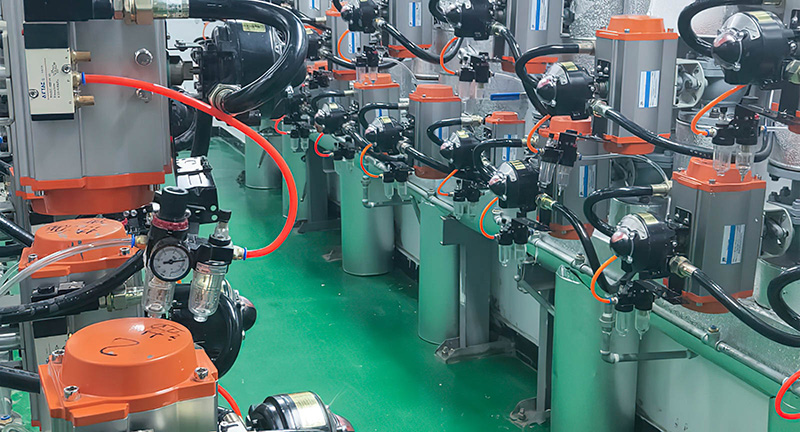


Control function: The lithium battery valve can control the flow, pressure and temperature of the fluid medium by adjusting the opening of the valve to meet the operating needs of the new energy system.
Safety protection function: The lithium battery valve has a safety protection function, which can automatically close when the system has abnormal conditions such as overpressure, overcurrent, and overtemperature, so as to prevent system damage and accidents.
Strong adaptability: lithium battery valves can adapt to the special requirements of various new energy systems, such as high temperature, high pressure, corrosion resistance, etc., to ensure the stable operation of the system.
Energy saving and environmental protection: The design and production process of lithium battery valves pay attention to energy conservation and environmental protection, and adopt advanced technology and materials to reduce energy consumption and environmental pollution.
Lithium battery valve is an important part in the field of new energy, and its excellent control, safety protection, adaptability, energy conservation and environmental protection provide a strong guarantee for the stable operation and sustainable development of the new energy system.
When selecting and using lithium battery valves, it is necessary to determine according to the specific type of new energy system and application scenarios, and it is also necessary to pay attention to the performance, quality and safety of the valve.
The global lithium battery industry has experienced explosive growth driven by electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems (ESS), consumer electronics, renewable energy integration, and smart manufacturing. As the demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to rise, battery production lines have become increasingly complex, automated, and controlled. In this environment, valves play a critical role in ensuring the safe, efficient, and precise movement of gases, liquids, slurries, electrolytes, and solvents throughout different stages of battery manufacturing.
Valves in lithium battery applications are not simply mechanical components — they are essential for chemical stability, process safety, fluid accuracy, contamination control, and plant-wide automation. From slurry mixing to electrolyte filling, gas purification to solvent recovery, vacuum systems to dry room utilities, valves ensure stable flow management, precise dosing, and loss-free chemical transport.
Battery plants require valves that can withstand corrosive chemicals, high purity requirements, vacuum conditions, and strict environmental controls. The most critical role of valves is to maintain consistency and safety in processes that directly affect battery quality, performance, and cycle life.
This 3500-word article provides an in-depth exploration of the application of valves in lithium battery manufacturing, covering process stages, valve types, material selection, automation trends, and safety considerations — all optimized with high-value SEO keywords such as lithium battery valves, electrolyte valves, vacuum valve for batteries, slurry valves, NMP valves, pneumatic actuator valves, chemical dosing valves, battery production valves, and mixing system valves.
2. Why Valves Are Critical in Lithium Battery Manufacturing
Lithium battery production involves chemicals and process conditions that must be controlled with extreme accuracy. Even minor deviations in fluid flow, impurity content, or pressure can compromise battery performance and safety.
Battery manufacturing requires precise control of:
Slurry viscosity
Electrolyte dosage
Gas flow rate
Vacuum pressure
Solvent recovery
Valves regulate each of these parameters.
Electrolytes are hazardous and flammable. Solvents like NMP and DMC can react with air or moisture. Valves ensure safe handling, containment, and distribution.
Valves prevent:
Metal contamination
Moisture intrusion
Slurry particle pollution
Electrolyte impurity mixing
Purity is essential for high-performance cells.
Modern giga-factories rely on automated valves controlled by:
PLC systems
Sensors
Actuators
SCADA systems
Automation guarantees efficiency, consistency, and worker safety.
Valves support:
Solvent recovery
Exhaust treatment
Wastewater treatment
Chemical recycling
These are essential for sustainable battery production.
3. Lithium Battery Production Stages That Use Valves
Valves are utilized across nearly every major step of lithium battery manufacturing. Key stages include:
Slurry mixing
Coating and drying
Calendering
Electrode cutting and forming
Cell assembly
Electrolyte filling
Formation and aging
Degassing
Packaging
Solvent recovery systems
Vacuum systems
Dry room operations
Gas distribution systems
Waste treatment
Each stage has unique requirements for flow control, pressure management, and chemical compatibility.
4. Applications of Valves in Slurry Mixing Systems
Slurry preparation is the foundation of electrode manufacturing. It involves mixing active materials, binders, conductive additives, and solvents.
Active materials: NCM, NCA, LFP, LCO
Conductive agents: carbon black, CNT
Binders: PVDF, SBR
Solvents: NMP (cathode), water (anode)
Diaphragm valves
Sanitary pneumatic valves
PTFE-lined ball valves
Powder feeding valves
NMP-resistant valves
Accurate solvent dosing
Binder mixing control
Powder unloading systems
Slurry transfer
Temperature-controlled water circulation
Agitator tank outlet isolation
Abrasion resistance
Chemical corrosion protection
Smooth internal surfaces to prevent slurry accumulation
Zero dead space design
Contamination-free construction
5. Valves Used in Coating and Drying Systems
Coating machines apply slurry onto copper/aluminum foil. Drying ovens remove moisture and solvent.
Hot air control valves
Steam valves
Exhaust valves
Solvent recovery valves
High-temperature butterfly valves
Oven temperature control
NMP vapor extraction
Airflow balancing
Solvent condensation system isolation
Drying systems operate under harsh thermal conditions, requiring durable, heat-resistant valves.
6. Valves in Calendering and Electrode Processing
Although calendering itself is mechanical, auxiliary systems require valves for:
Cooling water
Hydraulic oil
Compressed air
Vacuum systems
Valves used:
Ball valves
Pressure control valves
Hydraulic system valves
7. Applications in Cell Assembly (Winding & Stacking)
Vacuum conditions are required for:
Pouch cell stacking
Removing air pockets
Maintaining material cleanliness
Valves used:
High-vacuum gate valves
Angle valves
Vacuum butterfly valves
Used for:
Inert gas purging
Moisture removal
Dry room gas management
Types:
Nitrogen valves
Argon control valves
CO₂-free air valves
8. Electrolyte Filling Applications
Electrolyte filling is one of the most critical and sensitive steps in battery production.
LiPF₆ dissolved in EC/DMC/EMC
Additives (VC, FEC, PS)
Ultra-clean diaphragm valves
Precision metering valves
PTFE-lined isolation valves
Double-block valves
Absolutely no metallic contamination
High corrosion resistance
Precision dosing control
Leak-free design
Vacuum filling
Pressure filling
Dual-stage filling
Automatic electrolyte recycling
Valves ensure the electrolyte dosed is exactly accurate to prevent:
Overfilling
Underfilling
Gas entrapment
Battery swelling
9. Formation, Aging, and Degassing Systems
Batteries undergo controlled charge-discharge cycles.
Valves support:
Cooling systems
Safety exhaust systems
Fire suppression integration
Valves used:
Temperature control valves
HVAC air valves
Nitrogen safety valves
After formation, gas is removed to stabilize the cell.
Valves used:
Vacuum valves
Needle valves
High-accuracy vent valves
10. Solvent Recovery and Environmental Systems
NMP recovery and waste gas treatment are major requirements in lithium battery factories.
Valves used:
PTFE/PFA-lined ball valves
Anti-corrosion butterfly valves
High-vacuum valves
Functions:
Condensation
Separation
Distillation
Solvent recycling
Processes use:
Scrubbers
Heat exchangers
Oxidizers
Valves:
Corrosion-resistant valves
Flow control valves
Exhaust valves
11. Dry Room and Utility Systems
Lithium battery factories require extremely low humidity (≤1% RH).
Utilities that use valves:
Dehumidifiers
HVAC air control
Nitrogen distribution
Fire suppression
Types:
Actuated air valves
Pressure-regulating valves
Sanitary compressed air valves
12. Material Selection for Lithium Battery Valves
Preferred grades:
SS316L
SS304
Electropolished surfaces
Used for electrolyte and NMP resistance:
PTFE
PFA
PVDF
Chemical-resistant seals:
EPDM
FFKM (Kalrez)
Viton
Aluminum alloys
Stainless steel
Ceramic components
13. Types of Valves Commonly Used in Lithium Battery Factories
Diaphragm valves
Butterfly valves
Needle valves
Vacuum gate valves
Check valves
Relief valves
Metering valves
Solenoid valves
Double-block-and-bleed valves
Each has unique functions suited to specific battery processes.
14. Automation, Control, and Smart Valve Technology
Giga-factory automation requires intelligent valve systems.
Position feedback
Flow metering
Temperature monitoring
Predictive maintenance
PLC/MES connectivity
Pneumatic actuators
Electric actuators
Smart digital actuators
Automated valves enable:
Closed-loop filling systems
Real-time pressure control
Centralized plant automation
15. Challenges in Valve Engineering for Lithium Batteries
Electrolytes and solvents require special materials.
Even minimal contamination damages cells.
Leaks disrupt production stability.
Fire and explosion risks must be minimized.
Factories require long-life, high-cycle valves.
16. Future Trends in Lithium Battery Valve Applications
Advanced coatings and fluoropolymers.
Real-time chemical monitoring.
Industry 4.0 + AI automation.
Carbon-neutral solvent systems.
Designed for next-generation electrolytes and solid-state batteries.
17. Conclusion
Valves are indispensable components in lithium battery production, providing precise control over fluids, gases, electrolytes, solvents, and vacuum conditions. They support slurry mixing, coating operations, electrolyte filling, cell assembly, formation, recycling, and environmental systems. As the lithium battery industry continues to grow, valve technology will evolve toward smarter, cleaner, safer, and more automated solutions.
Manufacturers who invest in high-quality lithium battery valves will gain significant advantages in efficiency, product quality, and operational safety.
 RELATED
RELATED
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Comment
(0)